Osteoarthritis – the collective name of the dystrophic-degenerative diseases of the articular apparatus of various localization and etiology, who are in this similar clinical and morphological picture and the outcome and that are showing damage to the articular cartilage, subchondral bone formation, capsules, ligamentous apparatus.
Osteoarthritis – the most common pathology in rheumatology practice, according to medical statistics, about 1/5 of the whole population. Osteoarthritis is the cause of the significant reduction in the quality of life of approximately half of the patients, a large part of them becomes disabled. The incidence is directly dependent on the age: osteoarthritis rarely occurs in young age, will debut most often after 40-45 years of age, while people over 70 years of radiological symptoms are defined in the vast majority of cases. At a young age, the frequency of occurrence is approximately 6.5%, after 45 years of 14-15%, after 50 years – 27-30%, in persons over 70 years of age – 80 to 90%.
Most often when osteoarthritis in the disease process to involve the small joints of the brush (in women 10 times more often than men), inches, feet, intervertebral completion of the joints of the thoracic and cervical spine, as well as the knee and in the hip joints. Osteoarthritis of the knee and the hip joint occupies a leading place in the severity of clinical manifestations and negative impact on quality of life.
For osteoarthritis is characterised by the comprehensive defeat of the articular and auxiliary devices:
- inflammatory changes of the cartilage of the joint;
- participation in the disease process is necessary to bone structures;
- synovitis – inflammation of the inner lining of the joint;
- bunions – the defeat of the bags around the joints;
- reactive inflammation of the soft tissues (muscles, subcutaneous tissue, the ligamentous apparatus) are located in the projection of the involved joint.
Because the cause of arthritis are inflammatory changes, in a number of western countries is called the disease of arthritis. In Russian medicine, the terms arthritis and osteoarthritis occur as often and they mean one and the same disease process. The last time rheumatology practice, most often uses the term osteoarthritis, which will highlight the participation in the disease process is not only relatively to the joint, such as rolling connection, but that bone staff.
The consequences of arthrosis in the absence of adequate treatment, are a progressive reduction of range of motion in the affected joint, and immobilization.
Currently, access to the understanding of arthrosis radically changed: the disease is considered an aggressive process of destruction of the cartilage of the joint under the influence of inflammation, which requires a mandatory active anti-inflammatory treatment.
Synonyms: arthritis, osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis, deforming osteoarthritis.
Causes and risk factors
In the scientific community is ongoing dispute about the cause of the defeat of the joints. Some researchers are doing a main role of damage to the cartilage cover the surfaces, which under the influence of various factors, which leads to disruption of biomechanics of the joint and dystrofickém changes of the surrounding structures. Others, on the contrary, sees the key cause in the damage of the surface layers of the mating of bone structures, which form the joint (for example, due to violation of the microcirculation) and secondary changes believe dystrophy, and deterioration of the cartilage.
The factors that most often provoke the development of arthrosis:
- before acute traumatic damage to the joint (gap or tear ligaments, bruises, dislocations, intra-articular fracture, penetrating injury);
- excessive systematic load, associated with certain activities (for professional athletes, dancers, people in heavy physical labor, etc.);
- obesity;
- the local impact of low temperatures;
- a chronic disease in which suffer from local microcirculation (endocrine pathology, pathology of the vascular bed, and so on);
- delegated acute infectious diseases;
- changes in the hormonal background (pregnancy, menopause);
- autoimmune diseases, suggesting damage to the connective tissue;
- connective tissue dysplasia (a congenital weakness of this type of fabric, which accompanies the reaction increased mobility of the joints);
- genetic pathology – defect gene, which is localized on the 12 chromosome and encoding procollagen type II (COL2A1 gene), or a VDR gene that controls vitamin D-endocrine system;
- congenital structural and functional abnormalities of the articular apparatus;
- mature, elderly and senile age;
- vacuum of bone tissue (osteoporosis);
- chronic intoxication (including alcohol);
- delegated operational interventions on the joints.
In most cases osteoarthritis is poly-etiological nature, i.e. it develops when combined effects of multiple causal factors.
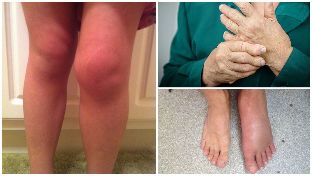
The symptoms of arthrosis
For arthrosis is not a typical acute clinical picture of changes of the joints are better, slowly growing the character, which is manifested by a gradual onset of symptomatology:
- pain;
- regularly the emerging crisis in the affected joint;
- deformation of the joint, discovering and growing with the development of the disease;
- stiffness;
- restrictions on mobility (reducing the amount of active and passive movements in the affected joint).
Pain when osteoarthritis wears blunt of a temporary character, to appear in the motion, on the background of the intense load to the end of the day (may be so intense that it does not allow the patient to fall asleep). Standing, is not the mechanical nature of the pain for arthrosis atypical and is indicative of active inflammation (subchondral bone, synovium, ligamentous apparatus, or periarticular muscles).
The majority of patients reported the presence of the so-called starting pain, emerging in the morning hours after waking up, or after a long period of inactivity, and which are held in the course of physical activities. Many patients define this condition as the need to "create a joint" or "diverge".
For arthrosis is a typical morning stiffness, which has a clear localization and carries a short-term character (no more than 30 minutes), sometimes it is perceived by patients as "feel like jelly" in the joints. Maybe the feeling of disturbance, stiffness.
In the development of the jet synovitidaa the main symptoms of arthritis of the joins:
- tenderness and local rise in temperature, the user-during palpation of the affected joint;
- the permanent nature of the pain;
- the increase in joint range, soft tissue swelling;
- the gradual reduction of range of motion.
For arthrosis is a typical increase in joint range, soft tissue swelling.
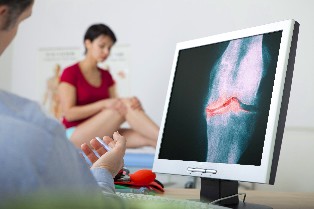
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis is based on the evaluation of anamnestic data, the characteristic manifestations of the disease, the results of instrumental methods of research. Demonstrative changes in general and biochemical analysis of blood for osteoarthritis are not typical, they only appear during the development of an active inflammatory process.
Basic instrumental methods of diagnosis of osteoarthritis radiography, in diagnostically obscure cases, it is recommended to carry out a computer or magnetic resonance tomography.
Osteoarthritis of the knee and the hip joint occupies a leading place in the severity of clinical manifestations and negative impact on quality of life.
Other diagnostic methods:
- arthroscopy;
- ultrasonography (evaluation of the thickness of the articular cartilage, the synovial sheath, a condition of joint bags, fluid);
- scintigraphy (evaluation of the status of bone tissue in the head of the bone, forming a joint replacement).
Treatment of arthrosis
Medical therapy:
- non-steroidal anti-antiinflammatory drugs – the relief of the pain syndrome and signs of inflammation in the focus;
- glucocorticosteroid hormones – intra-articular injection introduction for cupping phenomena synovitidaa; apply limited, in cases where it is necessary in the shortest possible time to eliminate the painful symptoms;
- antifermental agents (inhibitors of proteolysis) – prevent the progression of dystrofickéx and degenerative processes in cartilage and bone tissue;
- antispasmodics – allow to remove local muscle spasms in the affected segment;
- anabolic drugs – accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues;
- preparations aimed at correcting properties of blood, strengthen vascular walls, improve their elasticity and tissue regeneration – contributes to strengthening the walls of blood vessels of microcirculation stream, which provide sufficient blood supply to the damaged area;
- resources, improve the microcirculation;
- medications on the joints – regardless of their massive spread in the therapy of arthritis, in the large placebo-controlled trials of the clinical efficacy of this group of drugs is not proven.
Rehabilitation techniques used to treat osteoarthritis:
- massage regional muscles, improve blood circulation and the removal of a local spasm;
- active kinesiotherapy, i.e. performing the exercise in osteoarthritis using special simulators;
- physiotherapy in osteoarthritis;
- laser;
- ultrasound;
- therapeutic baths, mud and paraffin; and so on
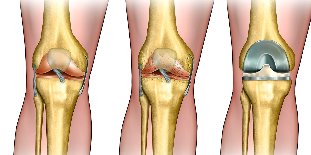
When the ineffectiveness of the mentioned methods of exposure, in the presence of complications resort to the surgical treatment of arthrosis:
- the decompression of meta-epiphysis and extended inside the bone of the blockade (decrease in intraosseous pressure in the affected area);
- corrective osteotomy;
- joint joints.
In the early stages of the disease applied by mechanical, laser unit (smoothing the surface of damaged cartilage, removal of devitalized land). This method effectively relieves painful, but it is a temporary effect – 2-3 years.
Possible complications and consequences
The consequences of arthrosis, especially in the absence of adequate treatment, are:
- progressive decrease in range of motion in the affected joint;
- immobilization.
Weather
Forecast for life favorable. The Friendlyness of the social and labour prognosis depends on timeliness of diagnosis and initiation of treatment, and decreases when tightening the decision of a question on surgical treatment of diseases in case of need.
Prevention
- Refusal of intense exertion, prolonged static stress on the affected joint.
- Wear the brace if necessary.
- Adherence to the diet in osteoarthritis, aimed at reducing body weight.
- Prevention of hypothermia.
- A complete treatment of acute injuries of the joints until full recovery with the obligatory ethos.
- Pharmacy observation at the occurrence of the symptoms of arthrosis.
































